Text copied!
SQL cross join
CROSS JOIN combines each row from one table with every row from another table. Typically, it is used to generate all possible combinations of rows from two or more tables.
The syntax of the SQL cross join generally looks like this :
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 CROSS JOIN table2;
• 'table1' and 'table2' refer to the two tables being joined together.
• 'column_name(s)' refer to the selected columns from the tables being joined together.
• It doesn't require any condition for joining two or more tables together. Since it can join tables without having any common columns.
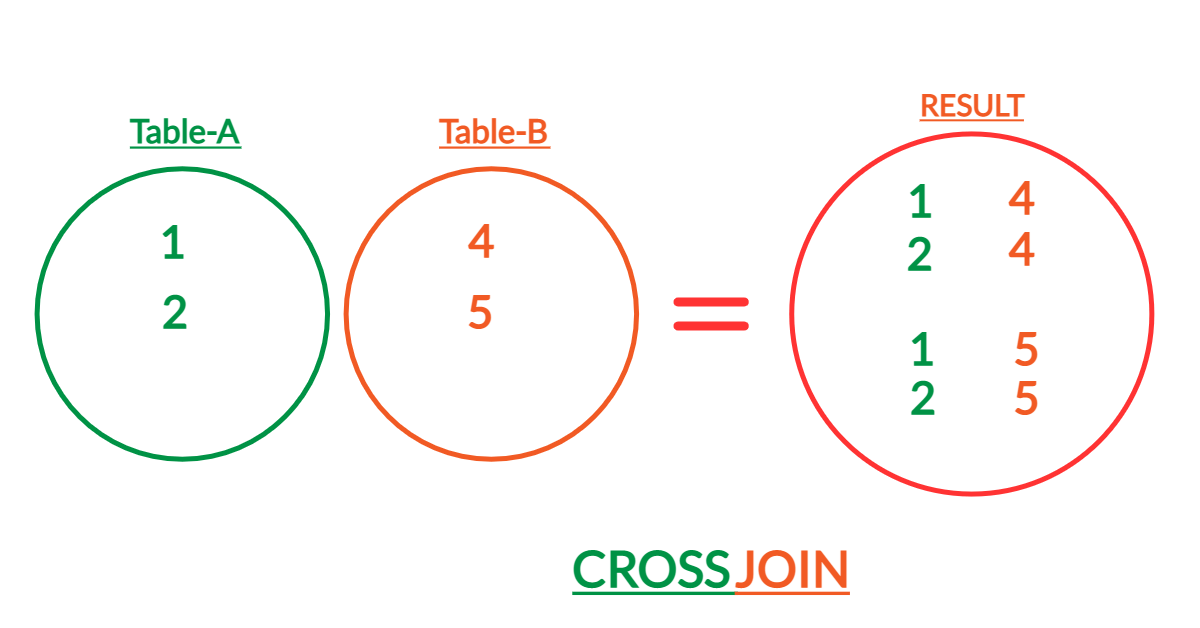
As seen in above image, SQL cross join produces a result set that includes each rows from 'Table-A' that is combined with every row from 'Table-B'.
Here's an example of how you might use the SQL cross join :
Let's suppose we have two tables :
[a] Employees Table :
→ It contains columns [Employee_Id], [Employee_Name], [Gender] and [Department_Id].
[b] Departments Table :
→ It contains columns [Department_Id] and [Department_Name].

1. Let's use SQL cross join to retrieve the employees names and their respective department names.
2. Please run the following SQL statement :
SELECT Emp.Employee_Name, Emp.Department_Id, Dpt.Department_Name
FROM [Employees] Emp
CROSS JOIN [Departments] Dpt
3. Above statement selects the columns from both tables. It returns all the rows from 'Table-A' that is combined with every row from 'Table-B' as the output.
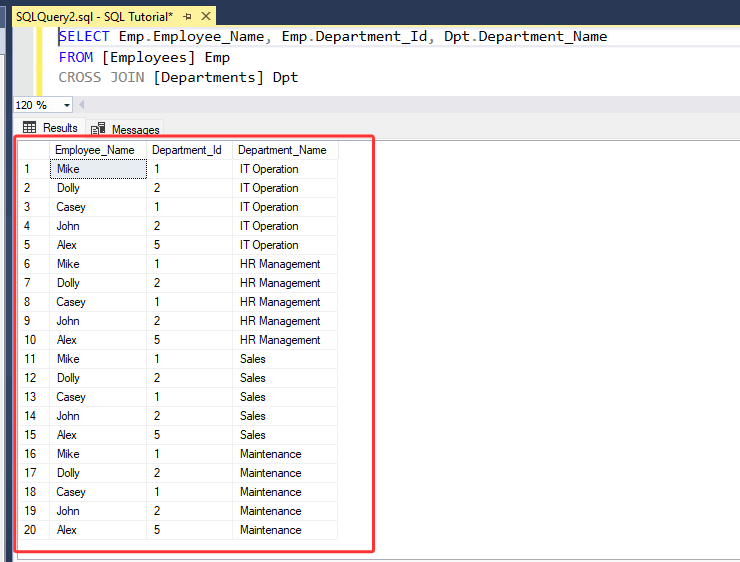
• As you have seen, Only specific selected columns ( [Employee_Name], [Department_Id] from "Employees" table and [Department_Name] from "Departments" table ) are returned.
• It returned each row from 'Table-A' that is combined with every row from 'Table-B'.
• It returned total 20 rows (5 * 4), because 'Table-A' has 5 rows and 'Table-B' has 4 rows.
That's it! You have successfully retrieved data using 'CROSS JOIN' statement.