Text copied!
SQL WITH TIES
Here's the syntax for using WITH TIES :
Here's an example of how to use WITH TIES in a SQL query :
1. Let assume you have a table called Employees with columns like Employee_id, Employee_Name, Gender, Salary, and Joining_Date.
SELECT TOP n WITH TIES column1, column2, column3 ...
FROM table_name
ORDER BY column_name DESC;
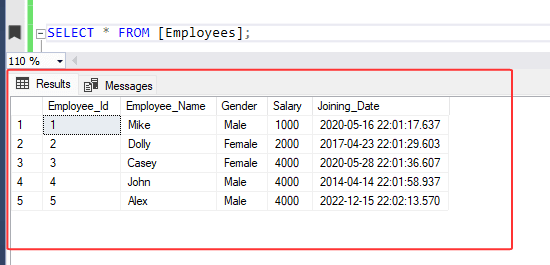
SELECT
TOP 2 WITH TIES
Employee_id, Employee_Name, Gender, Salary, Joining_Date
FROM [Employees]
ORDER BY Salary DESC;
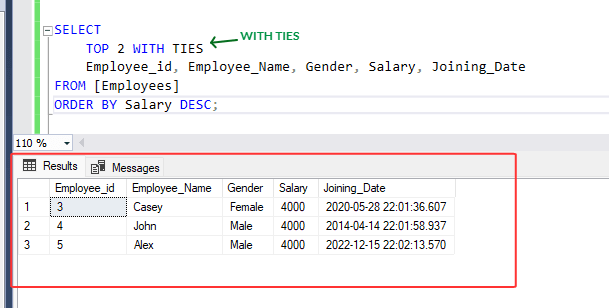
SELECT
TOP 2
Employee_id, Employee_Name, Gender, Salary, Joining_Date
FROM [Employees]
ORDER BY Salary DESC;
Frequently Asked Questions :
SQL with ties refers to retrieving additional rows that share the same value as the last row in an ordered result set.
Top 10 with ties in SQL retrieves the top 10 rows from a result set, including additional rows if they share the same value as the 10th row.
Select top 1 with ties means retrieving the top row from a result set, including additional rows if they share the same value as the top row.
Percentage with ties in SQL involves retrieving a specified percentage of rows from a result set, including additional rows if they share the same value as the last row in the specified percentage.
RELATED :
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Download SQL Server Management Studio SSMS
