Text copied!
JOIN clause
SQL clause is the specific part of a SQL statement which is used to perform various operations. It can be combined to create more complex queries to retrieve and manipulate data.
JOIN clause :
JOIN clause is used to combine two or more tables data by using a common column. It is often used with other clauses such as 'SELECT', 'FROM', 'HAVING' and 'ORDER BY' etc. to retrieve, specify table, filter, sort and manipulate data.
The syntax of the JOIN clause generally looks like this :
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
• Specify the column(s) name after the 'SELECT' keyword.
• 'column_name(s)' refer to the selected columns from the tables being joined together.
• Specify the table name after the 'FROM' keyword.
• 'table1' and 'table2' refer to the two tables being joined together.
• 'ON' clause is used to specify the conditions for joining two or more tables together.
• There are several types of SQL joins, by default 'JOIN' keyword is treated as 'INNER JOIN'.
Here's an example of how you might use the JOIN clause :
Let's suppose we have two tables :
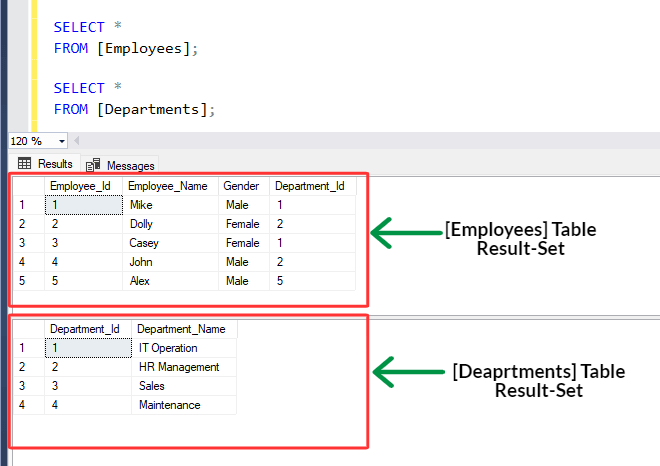
[a] Employees Table :
→ It contains columns [Employee_Id], [Employee_Name], [Gender] and [Department_Id].
[b] Departments Table :
→ It contains columns [Department_Id] and [Department_Name].
1. Let's use SQL inner join to retrieve the employees names and their respective department names by joining the [Employees] and [Departments] tables together based on matching values in both the tables.
2. Please run the following SQL statement :
SELECT Emp.Employee_Name, Emp.Department_Id, Dpt.Department_Name
FROM [Employees] Emp
INNER JOIN [Departments] Dpt
ON Emp.Department_Id = Dpt.Department_Id
3. Above statement selects the columns from both tables based on the matching values in the 'Department_Id' column and returns the resulting data as the output.
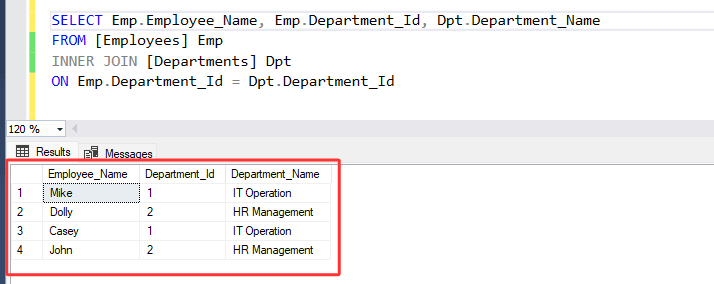
• As you have seen, Only specific selected columns ( [Employee_Name], [Department_Id] from "Employees" table and [Department_Name] from "Departments" table ) are returned.
• It returned only the rows where the [Department_Id] column has values of '1' or '2' because these are the only values that exist in both tables.
That's it! You have successfully retrieved data using 'JOIN' clause.