Text copied!
UNION operator
In SQL, Operators are special character, symbol or a keyword that is used to perform some specific operations. For example : comparing data
SQL operators are commonly used with SQL statements to retrieve, filter, and manipulate data.
UNION operator :
UNION operator is used to merge the result of multiple SELECT statements into a single result by eliminating duplicate rows.
While using UNION operator, ensure that column_name(s) and their data types should be in the same order across all SELECT statements.
The syntax of the UNION operator generally looks like this :
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
UNION
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table2;
• Specify the column(s) name after the 'SELECT' keyword.
• Specify Asterisk (*) symbol to selects all columns from the table after the 'SELECT' keyword.
• Specify the table name after the 'FROM' keyword.
• 'table1' and 'table2' refer to the two tables being merged together.
• 'UNION' keyword combines the result set of multiple SELECT statements into a single result by eliminating duplicate rows.
Here's an example of how you might use the UNION operator :
Let's suppose we have two tables :
[a] Employees Table :
→ It contains columns [Employee_Id], [Employee_Name], [Gender] and [Salary].
[b] Employees_2 Table :
→ It contains all columns same as '[Employees] table' with same data types and order. Except '[Age]' column.

1. Please ensure that each column_name(s) and their data types are in the same order across all SELECT statements.
For example, let's see what happens if we run the below statement :
SELECT *
FROM [Employees]
UNION
SELECT *
FROM [Employees_2];

An error is thrown indicating that while performing 'UNION' operation, number of columns must be the same in all SELECT statements.
The error occurred because we specified 'Asterisk' (*) symbol that selects all columns from the table where [Employees_2] table contains '[Age]' column which is absent in [Employees] table. Therefore, we need to specify column_name(s) explicitly in all SELECT statements.
2. Please run the following SQL statement :
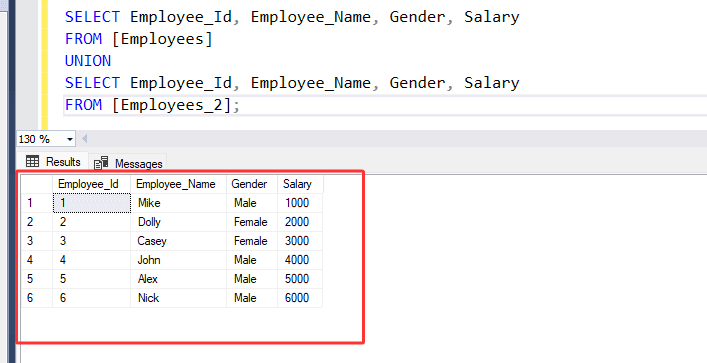
SELECT Employee_Id, Employee_Name, Gender, Salary
FROM [Employees]
UNION
SELECT Employee_Id, Employee_Name, Gender, Salary
FROM [Employees_2];
3. Above statement merges the result sets of both employee tables into a single result set for all selected columns. It eliminated duplicate rows. Hence only 6 rows are returned.
That's it! You have successfully merged data using 'UNION' operator.