Text copied!
EXISTS operator
In SQL, Operators are special character, symbol or a keyword that is used to perform some specific operations. For example : comparing data
SQL operators are commonly used with SQL statements to retrieve, filter, and manipulate data.
EXISTS operator :
EXISTS operator is used to check whether rows exists in a subquery or not. It retrieves only those rows that exists in a subquery. When a query is placed inside the 'parentheses ( )' of another query, it is referred as 'subquery' or 'nested query'.
The syntax of the EXISTS operator generally looks like this :
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE EXISTS (subquery);
• Specify the column(s) name after the 'SELECT' keyword.
• Specify Asterisk (*) symbol to selects all columns from the table after the 'SELECT' keyword.
• Specify the table name after the 'FROM' keyword.
• Specify the conditions after the 'WHERE' keyword.
• Specify the subquery after 'EXISTS' keyword.
Here's an example of how you might use the EXISTS operator :
Let's suppose we have two tables :
[a] Employees Table :
→ It contains columns [Employee_Id], [Employee_Name], [Gender] and [Salary].
[b] Employees_2 Table :
→ It contains all columns same as '[Employees] table' with same data types and order. Except '[Age]' column.
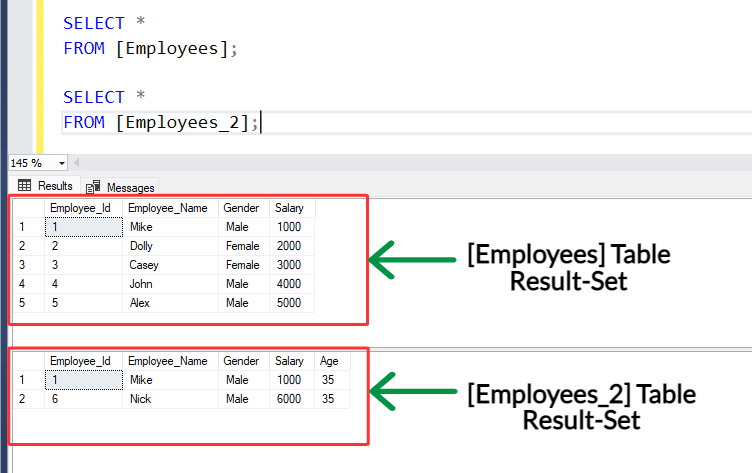
Let's assume you want to check and retrieve employee data from [Employees] table if there are any rows that have a matching Employee_Id with the [Employees_2] table.
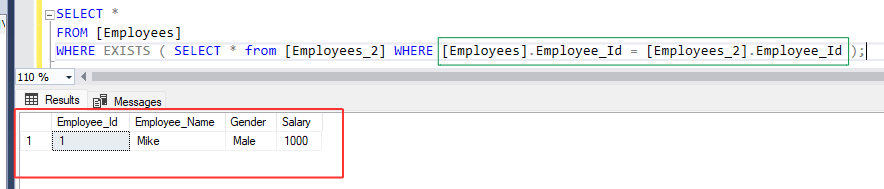
Run below SQL statement :
SELECT *
FROM [Employees]
WHERE EXISTS ( SELECT *
FROM [Employees_2]
WHERE Employees].Employee_Id = [Employees_2].Employee_Id );
Above statement will retrieve employee data from [Employees] table where Employee_Id is 1, as it is the only matching Employee_Id in both the tables.