Text copied!
SQL CTE
In SQL, CTE stands for Common Table Expression. A CTE is like a temporary result set that you can use within SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.
CTEs make it easier to understand and handle complex SQL queries.
Here's the basic syntax of a CTE :
WITH cte_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
AS
(
-- CTE query
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE conditions
)
-- Main query using the CTE
SELECT *
FROM cte_name;
• WITH : This is the keyword to initiate a CTE.
• cte_name : This is the name you give to your CTE.
• (column1, column2, column3, ...) : These are optional. You can specify the column names that will be returned by the CTE.
• AS : This keyword starts the definition of the CTE.
• ( ) : Inside these parentheses is the query that defines the CTE.
• SELECT * FROM cte_name : This is the main query that utilizes the CTE.
Here's an example to illustrate the usage of a CTE :
1. Let assume you have a table called Employees with columns like Employee_id, Employee_Name, Gender, Salary, and Joining_Date.
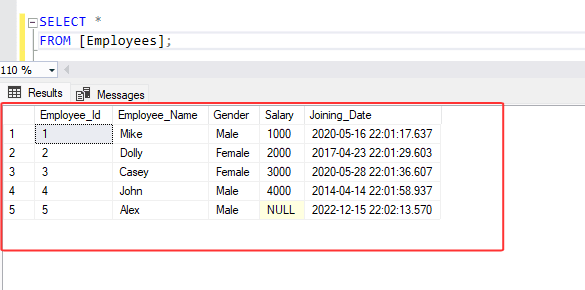
2. Now, you want to create a CTE that holds only those employees whose salary exceeds 1000.
3. Run below SQL statement :
WITH HR_Employees AS (
SELECT Employee_id, Employee_Name, Gender, Salary, Joining_Date
FROM Employees
WHERE Salary > 1000
)
SELECT *
FROM HR_Employees;
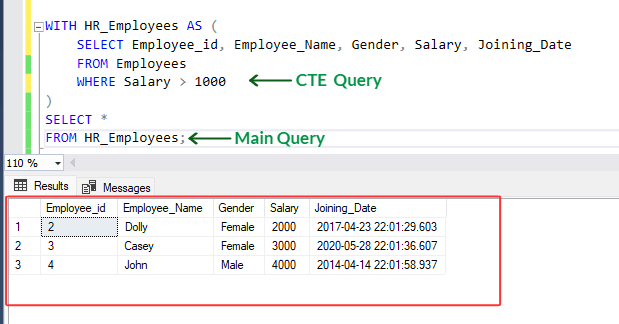
4. In this example, HR_Employees is the name given to the CTE. It holds only the employees whose salary is higher than 1000. The main query then selects all columns from this CTE, fetching the details of those employees.
That's it! You've just seen how to use a CTE statement in SQL. Hope it was clear and helpful!