Text copied!
SQL Aliases
In SQL, 'Alias' is used to assign an alternate name to a table or column in a query. It uses "AS" keyword to assign an alternate name.
Here's the ideal syntax :
SELECT column1 AS alias_name, column2 AS alias_name, ... FROM table_name AS alias_name;
Here's an example of Alias :
Let's suppose we have two tables :
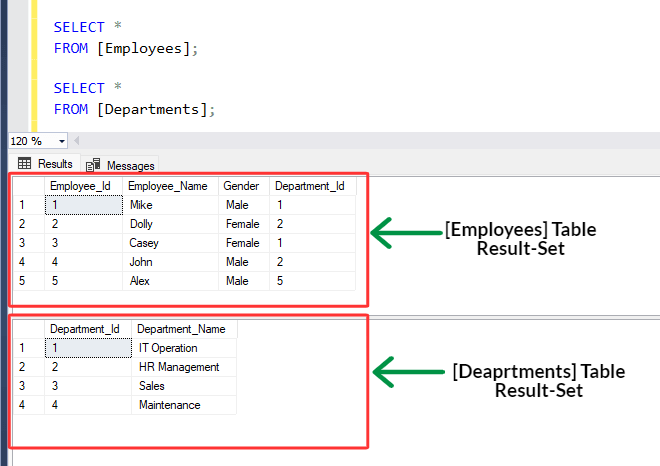
[a] Employees Table :
→ It contains columns [Employee_Id], [Employee_Name], [Gender] and [Department_Id].
[b] Departments Table :
→ It contains columns [Department_Id] and [Department_Name].
1. Let's assume you want to retrieve the "Employee_Name" column as "Name" only and their respective department names by joining the [Employees] and [Departments] tables together based on matching values in both the tables.
2. Please run the following SQL statement :
SELECT Emp.Employee_Name AS [NAME], Emp.Department_Id, Dpt.Department_Name
FROM [Employees] AS Emp
INNER JOIN [Departments] AS Dpt
ON Emp.Department_Id = Dpt.Department_Id;
3. Above statement selects the columns from both tables based on the matching values in the 'Department_Id' column and returns the resulting data as the output.

In this example, [Employees] and [Departments] tables are aliases for 'Emp' and 'Dpt' respectively.
[Name] is a alias assigned to 'Employee_Name' column. This can be useful when you want to assign alternative names to columns in the result set.