Text copied!
SQL Logical operators
In SQL, Operators are special character, symbol or a keyword that is used to perform some specific operations. For example : comparing data
SQL operators are commonly used with SQL statements to retrieve, filter, and manipulate data.
SQL logical operators can be used to combine multiple conditions in 'WHERE' clause to retrieve specific data.
Overview of SQL logical operators :
• AND
• OR
• NOT
Let's assume we have a table named "[Employees]".
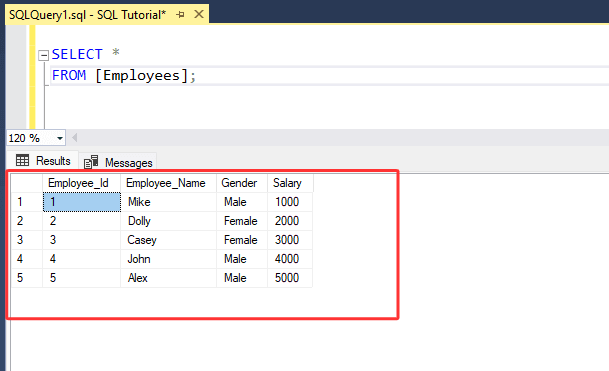
1. AND :
It is a operator that returns 'TRUE' if both or all the specified conditions are true in 'WHERE' clause.
Write a SQL statement to retrieve employees data from [Employees] table where Gender is 'Female' and Salary is greater than 5000.
SELECT *
FROM [Employees]
WHERE Gender = 'Female' AND Salary > 5000;
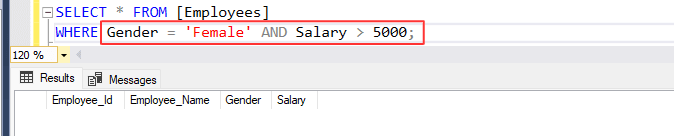
By using 'AND' operator, above statement returned zero rows because both/all conditions in 'WHERE' clause were not satisfied, only the first condition was satisfied. The [Employees] table doesn't contain any row where employee's gender is 'Female' and as well as their salary is greater than 5000.
2. OR :
It is a operator that returns 'TRUE' if any or at least one condition is true in 'WHERE' clause.
Write a SQL statement to retrieve employees data from [Employees] table where Gender is 'Female' or Salary is greater than 5000.
SELECT *
FROM [Employees]
WHERE Gender = 'Female' OR Salary > 5000;
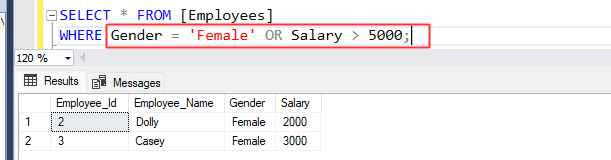
By using 'OR' operator, above statement returned two rows because the first condition in 'WHERE' clause were satisfied. The [Employees] table contains 2 rows where employee's gender is 'Female' and it doesn't contain any row where salary is greater than 5000.
3. NOT :
It is a operator that reverses or negates the conditions in 'WHERE' clause.
Write a SQL statement to retrieve employees data from [Employees] table where Gender is not 'Male'.
SELECT *
FROM [Employees]
WHERE NOT Gender = 'Male';
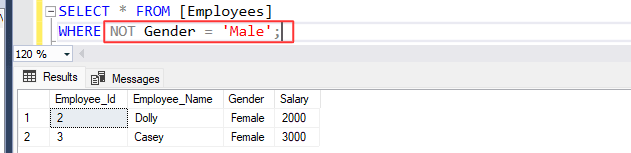
By using 'NOT' operator, above statement returned two rows because the condition in 'WHERE' clause were reversed. The [Employees] table contains 2 rows where employee's gender is not 'Male'.