Text copied!
Define Transaction in DBMS
In DBMS, a transaction is a way to execute multiple statements together. When you group statements into a transaction, they either all succeed or all fail. If everything goes smoothly, the changes made by the transaction are saved. However, if any part of the transaction encounters an error, all changes are undone or "rolled back."
Consider a simple scenario where you're transferring money from one bank account to another. You want both the deduction from one account and the addition to the other to happen together. If either step fails (like insufficient funds), you want to cancel the whole transaction.
Here's a simplified syntax for SQL Server transaction :
BEGIN TRANSACTION; -- Start the transaction
-- SQL statements to perform within the transaction
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION; -- If any error occurs, rollback the transaction
COMMIT TRANSACTION; -- If everything goes well, commit the transaction
BEGIN TRANSACTION :
BEGIN TRANSACTION marks the start of a transaction. You can define it as "BEGIN TRANSACTION," "BEGIN TRAN," or "BEGIN TRANSACTION [Transaction_Name]" to initiate a transaction.
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION :
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION undoes the changes made in the transaction if an error occurs. You can define it as "ROLLBACK TRANSACTION," "ROLLBACK TRAN," or "ROLLBACK TRANSACTION [Transaction_Name]" to rollback a transaction.
COMMIT TRANSACTION :
COMMIT TRANSACTION saves the changes made in the transaction to the database if everything was successful. You can define it as "COMMIT TRANSACTION," "COMMIT TRAN," or "COMMIT TRANSACTION [Transaction_Name]" to rollback a transaction.
Here's a simple example of a transaction in SQL Server :-
This is an example where all the queries within the transaction run without any errors :
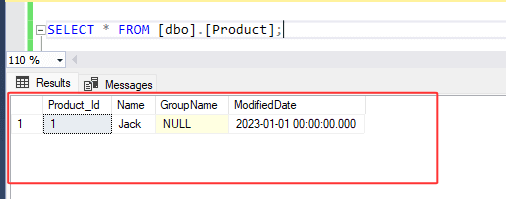
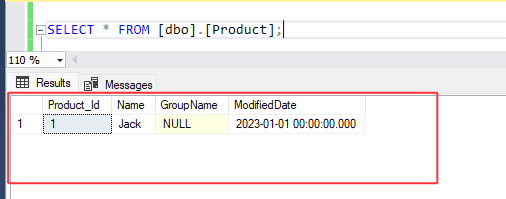
1. Let's consider a table named '[Product]' containing the following values :
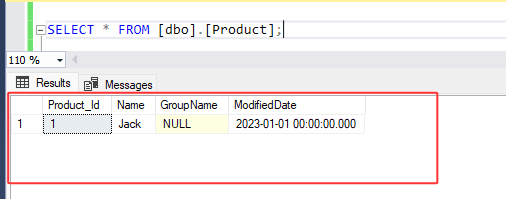
2. Now, let's examine the ROLLBACK TRANSACTION query below, which rolls back changes whether the queries within the transaction succeeded or failed. Run below transaction statement :
BEGIN TRANSACTION ABC
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Product] (
[Product_Id], [Name], [GroupName], [ModifiedDate] )
VALUES
(2, 'Soap', 'Group-B', '2023-01-01 00:00:00.000');
UPDATE [dbo].[Product]
SET [GroupName] = 'Sales'
WHERE [Product_Id] = 1;
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION ABC
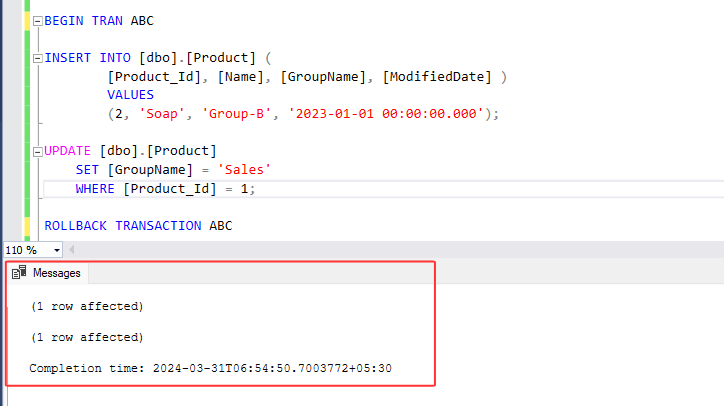
3. In this example, we've named our transaction 'ABC' and included two SQL statements within it. We're demonstrating the rollback query, which undoes any changes made, regardless of whether the queries within the transaction succeeded or failed. Rollback always reverts all changes back to its original state.
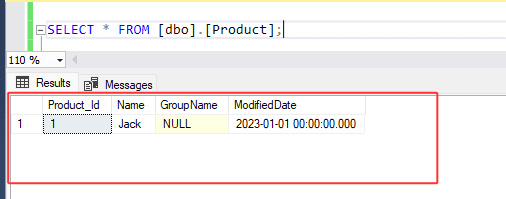
Check the output below, both insert and update queries within the transaction command are successful and therefore, no changes are made to the product table. To apply any changes defined within the transaction, we must commit.
4. Now, let's examine the COMMIT TRANSACTION query below, which commits changes only if all the queries within the transaction are successful. Run below transaction statement :
BEGIN TRANSACTION ABC
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Product] (
[Product_Id], [Name], [GroupName], [ModifiedDate] )
VALUES
(2, 'Soap', 'Group-B', '2023-01-01 00:00:00.000');
UPDATE [dbo].[Product]
SET [GroupName] = 'Sales'
WHERE [Product_Id] = 1;
COMMIT TRANSACTION ABC
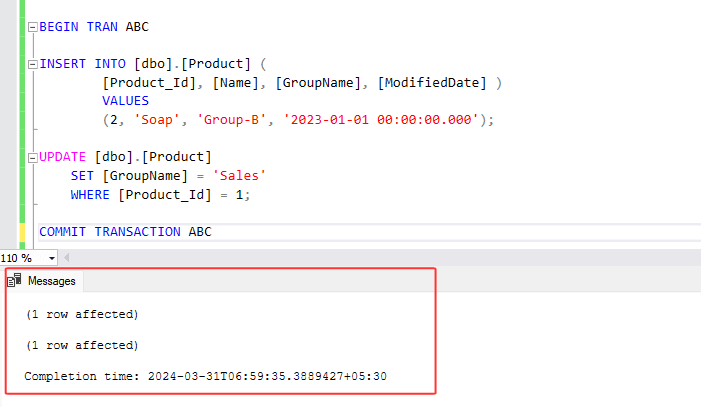
5. In this example, we've named our transaction 'ABC' and included two SQL statements within it. We're demonstrating the commit query, It applies changes only if all the queries within the transaction are successful.
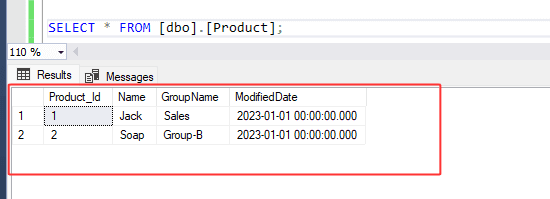
Look at the results below. Both insert and update queries within the transaction command were successful, and therefore, changes were applied to the product table because we used the commit transaction command. The group name has been changed to 'sales', and a new record with product ID 2 has been added.
This is an example where one of the queries within the transaction encounters an error :
1. Let's consider a table named '[Product]' containing the following values :
2. Now, let's examine the ROLLBACK TRANSACTION query below, which rolls back changes whether the queries within the transaction succeeded or failed. Run below transaction statement :
BEGIN TRANSACTION ABC
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Product] (
[Product_Id], [Name], [GroupName], [ModifiedDate] )
VALUES
(2, 'Soap', 'Group-B', '2023-01-01 00:00:00.000');
UPDATE [dbo].[Product]
SET [GroupName] = 'Sales'
WHERE [Product_Id] = 'A';
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION ABC
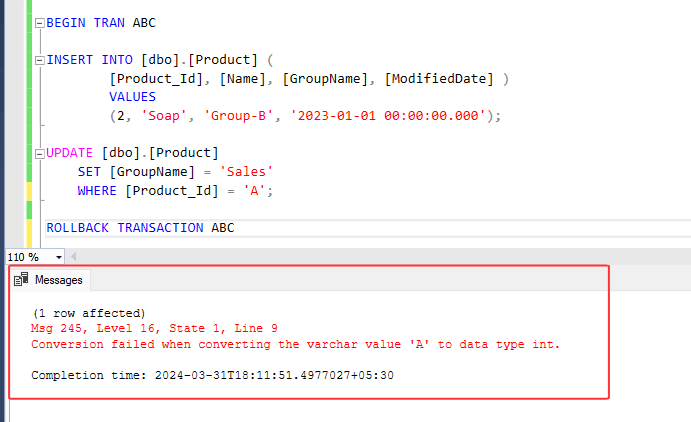
3. In this example, we've named our transaction 'ABC' and included two SQL statements within it. We're demonstrating the rollback query, which undoes any changes made, regardless of whether the queries within the transaction succeeded or failed. Rollback always reverts all changes back to its original state.
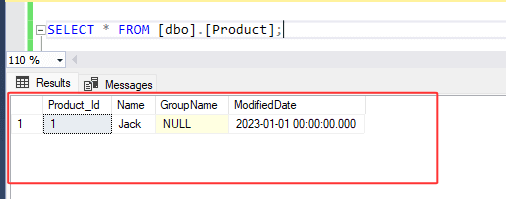
Check the output below, insert query is successful but update query within the transaction command is failed because we specified 'A' as the product ID, which is a string and cannot serve as a valid product Id. And therefore, no changes are made to the product table. To apply any changes defined within the transaction, we must commit.
4. Now, let's examine the COMMIT TRANSACTION query below, which commits changes only if all the queries within the transaction are successful. Run below transaction statement :
BEGIN TRANSACTION ABC
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Product] (
[Product_Id], [Name], [GroupName], [ModifiedDate] )
VALUES
(2, 'Soap', 'Group-B', '2023-01-01 00:00:00.000');
UPDATE [dbo].[Product]
SET [GroupName] = 'Sales'
WHERE [Product_Id] = 'A';
COMMIT TRANSACTION ABC
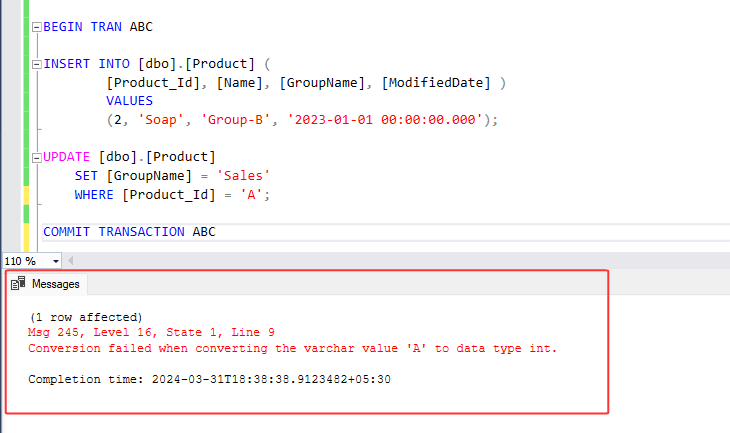
5. In this example, we've named our transaction 'ABC' and included two SQL statements within it. We're demonstrating the commit query, It applies changes only if all the queries within the transaction are successful.
Look at the results below. Insert query is successful but update query within the transaction command is failed because we specified 'A' as the product ID, which is a string and cannot serve as a valid product Id. and therefore, no changes were applied to the product table. Consequently, the system automatically rolled back the changes made by the insert query.