Text copied!
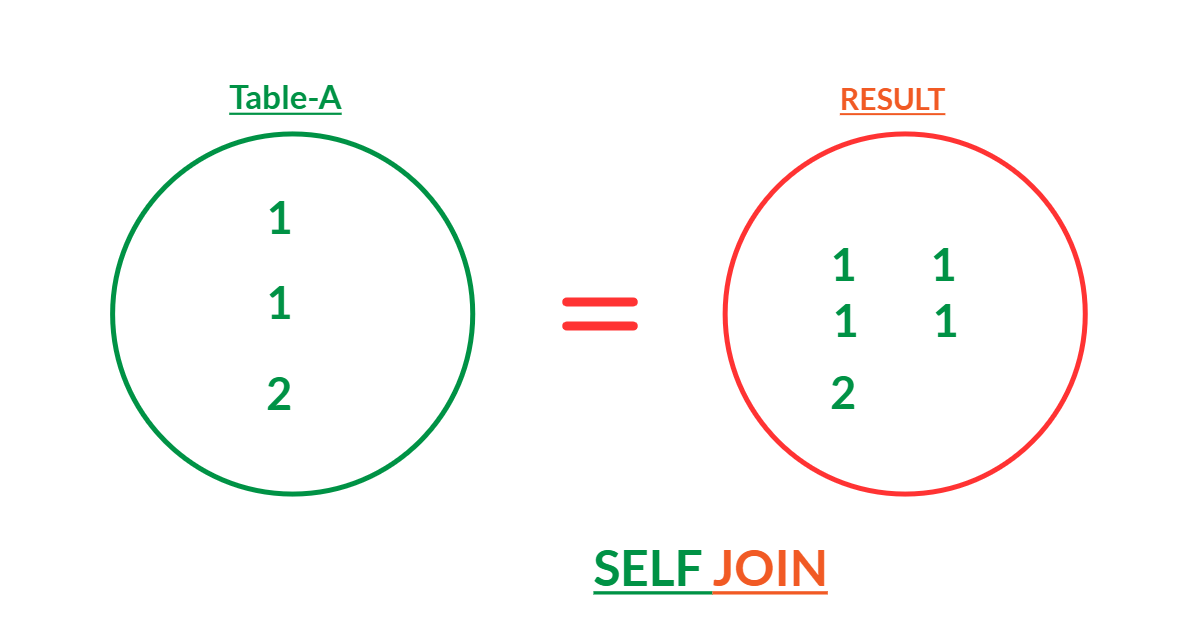
SQL self join
The syntax of the SQL self join generally looks like this :
Here's an example of how you might use the SQL self join :
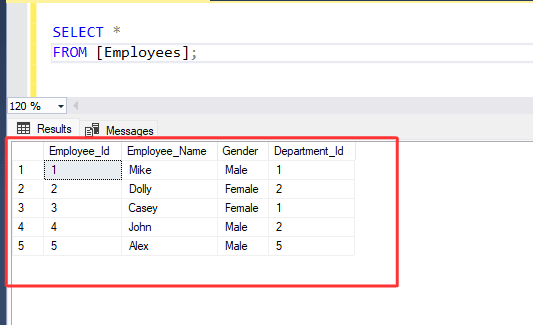
Let's suppose we have a table :
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 t1 JOIN table1 t2 ON t1.column_name = t2.column_name;
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1 t1, table1 t2
WHERE condition;
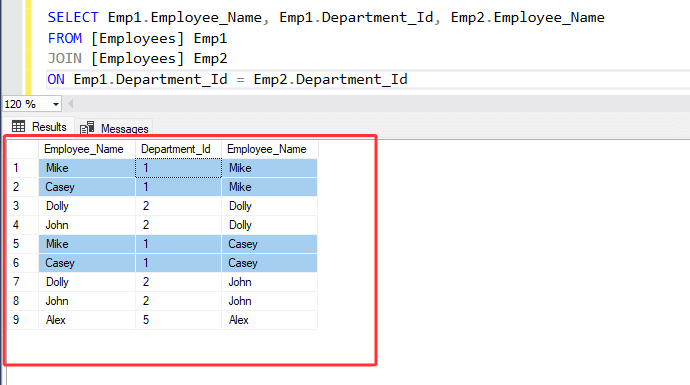
SELECT Emp1.Employee_Name, Emp1.Department_Id, Emp2.Employee_Name
FROM [Employees] Emp1
JOIN [Employees] Emp2
ON Emp1.Department_Id = Emp2.Department_Id
Frequently Asked Questions :
A self join in SQL is when a table is joined with itself.
The difference between inner join and self join in SQL is that inner join involves joining two separate tables, while self join involves joining a table with itself.
An outer join in SQL combines rows from two tables even if there is no match, while a self join involves joining a table with itself.
Self join in SQL involves joining a table with itself, while a Cartesian join combines every row from one table with every row from another table.
RELATED :
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management System: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Api Integration And Automation Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Backend Systems For Scalable Products: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Digital Platform Engineering Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Application Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboards For Companies: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Services: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Scalable Digital Platforms: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Product Engineering: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Executive Buyer Guide for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Framework for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Implementation Roadmap for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Common Failure Patterns for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Security and Governance Lens for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Scaling Playbook for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Build vs Buy Decision Model for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: KPI and Reporting Strategy for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Growth-Focused Execution Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Ecommerce Software For Businesses: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Auction Software Platform: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cricket Tournament Management Software: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Membership Billing Software: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Gym Management Software Platform: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Modernization Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Query Optimization For Enterprise Applications: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Scalability Consulting: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Database Architecture And Engineering Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Sql Performance Optimization Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Customer Analytics Platform Engineering: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Ecommerce Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Decision Intelligence Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Analytics Engineering Services For Businesses: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Analytics Platform Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Batch And Real-Time Data Pipeline Engineering: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Etl Automation Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Api Data Integration Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Integration Pipeline Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Etl Pipeline Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Modern Data Warehouse Consulting: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Cloud Data Warehouse Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Data Warehousing Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Implementation Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Data Warehouse Architecture For Companies: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Kpi Dashboard Development For Companies: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Reporting System Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Executive Dashboard Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Power Bi Dashboard Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Business Intelligence Dashboard Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Architecture Consulting For Startups: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Subscription Platform Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Multi-Tenant Saas Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Engineering Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Saas Product Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Founder-Led Product Engineering Partner: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Rapid Prototype To Mvp Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Mvp App Development For Startups: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Product Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Startup Mvp Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Corporate Web Platform Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Secure Enterprise Web Portal Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Scalable Web Application Architecture: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Web Application Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Business Software Solutions: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Enterprise Custom Application Development: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Bespoke Software Development For Businesses: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Services: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Risk Mitigation Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Adoption and Enablement Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Operational Excellence Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Architecture Due Diligence for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Procurement Strategy Brief for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Leadership FAQ Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Product-Led Growth Lens for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Enterprise Rollout Framework for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Integration Readiness Guide for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Change Management Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: 90-Day Execution Plan for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Vendor Evaluation Checklist for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: KPI and Reporting Architecture for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Build vs Buy Analysis for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Scalability Strategy for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Security and Governance Model for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Failure Patterns and Recovery for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Implementation Blueprint for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Cost, Timeline, and ROI Playbook for Modern Businesses
Custom Software Development Company: Executive Decision Framework for Modern Businesses
Download SQL Server Management Studio SSMS
