Text copied!
SQL Data Types
A data type is like a tag that tells the computer what kind of data/information it's dealing with. It helps computers to manage data effectively and in a structured manner.
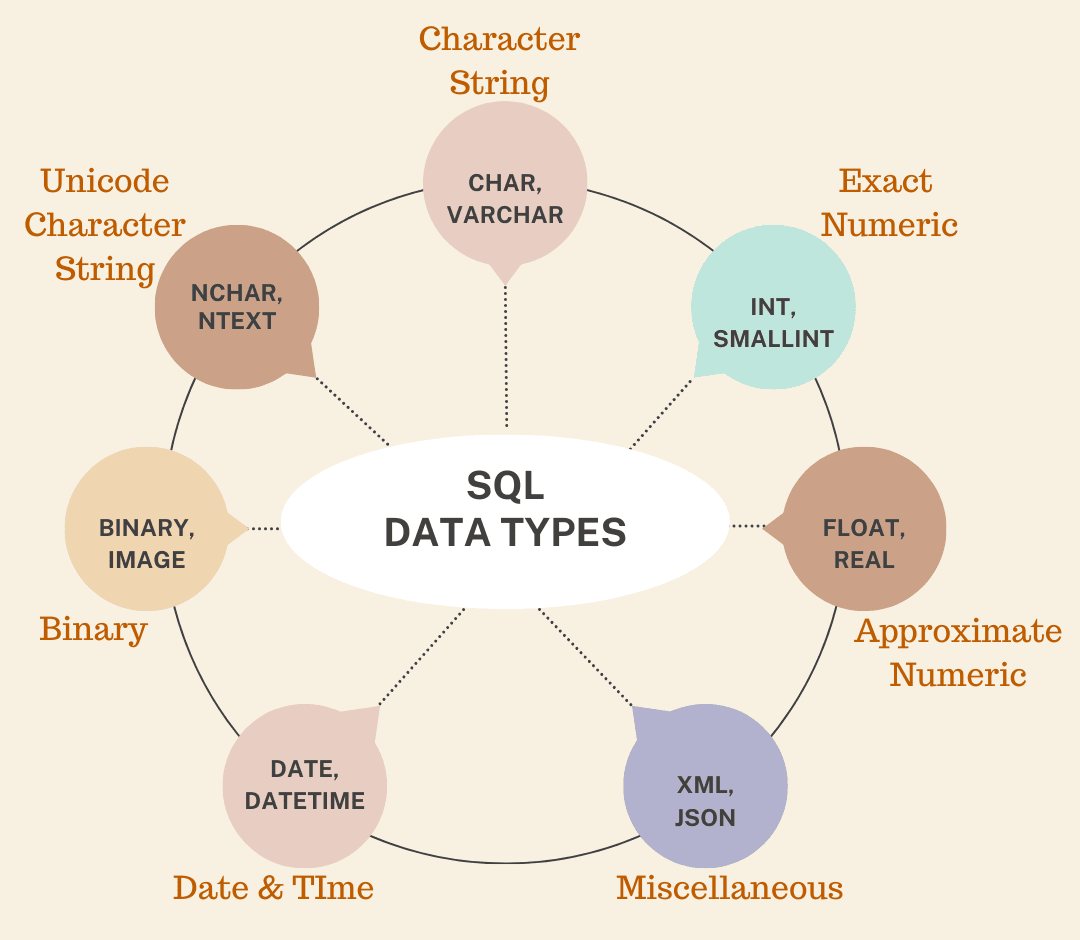
SQL data types define what type of data can be stored, the range of values it can hold and the operations that can be performed on it.
It can be defined during the table creation by using "CREATE TABLE" statement or added to an existing table using "ALTER TABLE" statement.
Here's an example of SQL data types :
"INTEGER" data types can be used to store whole numbers, while "CHARACTER" data types can store strings of text.
CREATE TABLE Student (
[StudentId] INT,
[Name] VARCHAR(100)
);

SQL data types that can be grouped into the following categories :
1. Numeric data types :
These data types are used to store numeric values such as integers, decimals and floating-point numbers.
BIT :
* Used to store binary data, either 0 or 1.
* Range : 0 to 1
* Storage : 1 byte
TINYINT :
* Used to store integer values.
* Range : 0 to 255 (signed) or
-128 to 127 (unsigned)
* Storage : 1 byte
SMALLINT :
* Used to store integer values.
* Range : -32,768 to 32,767 (signed) or
0 to 65,535 (unsigned)
* Storage : 2 bytes
INT :
* Used to store integer values.
* Range : -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 (signed) or
0 to 4,294,967,295 (unsigned)
* Storage : 2 bytes
FLOAT:
* Used to store approximate numerical values with a decimal point.
* Range : -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 (signed) or
0 to 4,294,967,295 (unsigned)
* Storage : 4 to 8 bytes
BIGINT:
* Used to store integer values.
* Range : -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 (signed) or
0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 (unsigned).
* Storage : 8 bytes
DECIMAL :
* Used to store fixed-point decimal numbers.
It is defined with two parameters: precision
and scale. The precision parameter specifies
the total number of digits that can be stored,
both to the left and to the right of the decimal
point. The scale parameter specifies number
of digits that can be stored to the right of the
decimal point.
Example :
CREATE TABLE Products (
[ProductID] int PRIMARY KEY,
[Price] decimal(10,2)
);
NUMERIC :
* NUMERIC is similar to the DECIMAL type.
The only difference, value that is too large
to fit into the specified precision and scale
of a decimal value, an error is generated.
2. Character string data types :
These data types are used to store character strings such as names, addresses and other textual data.
CHAR :
* Used to store fixed-length character strings.
When defining a char column, you must
specify the maximum number of characters
that can be stored in the column.
For Example :
if you define a char(10) column
and insert the value 'hello'.
VARCHAR :
* VARCHAR is similar to the CHAR data type,
The difference, varchar columns only take
up as much space as is required to store
the actual data being stored, plus two extra
bytes to store the length of the data.
For example :
if you define a varchar(10) column and
insert the value 'hello' into the column,
the value will only take up five bytes
(plus two bytes for the length), rather
than the full ten bytes that would be used
by a char(10) column.
VARCHAR (max) :
* VARCHAR(max) is a variant of varchar
data type that allows you to store
variable-length character strings of up to
2GB in size (2^31-1 bytes).
It is commonly used to store large text
values such as long articles, email
messages, or XML data.
For example :
CREATE TABLE Customer (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Description VARCHAR(MAX)
);
3. Date/Time data types :
These data types are used to store dates and times in various formats.
DATETIME :
* Used to store both the date and time
in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS format,
such as '2023-04-14 12:30:45'
* Range : January 1, 1753, to December 31, 9999,
and
times from 00:00:00 to 23:59:59.997.
* Storage : 8 bytes
DATE :
* Used to store the date in YYYY-MM-DD format,
such as '2023-04-14'
TIME :
* Used to store the time in HH:MM:SS format,
such as '12:30:45'
4. Unicode character string data types :
These data types are designed to store a broad range of characters and symbols from various languages and character sets.
NCHAR :
* Used to store a fixed-length Unicode
character string of n characters,
where n is a number from 1 to 4,000.
NVARCHAR :
* Used to store a variable-length Unicode
character string of up to n characters,
where n is a number from 1 to 4,000.
NVARCHAR(MAX) :
* Used to store a variable-length
Unicode character string of up
to 2^31-1 (2,147,483,647)
characters.