Text copied!
Temp table
Temporary tables are commonly known as 'temp tables' and it is created to store data temporarily during the execution of a query and are automatically deleted when the session ends.
Session :
When a user logs in and executes SQL statement to access SQL Server database engine, a connection is established. This connection is referred to as a 'session'. When a user closes the current query tab or logs out from the SQL Server database engine, the current session is ended.
There are two types of Temporary tables :
[a] Local temporary table :
Local temporary tables are only visible to the session that created them and are dropped automatically when the session ends. To create it, place single hash (#) before the table name.
Here's the syntax :
CREATE TABLE #TempTableName (
Column1 data_type,
Column2 data_type,
...
);
[b] Global temporary table :
Global temporary tables are accessible to all sessions, but they are dropped automatically when the session that created them ends. To create it, place double hash (##) before the table name.
Here's the syntax :
CREATE TABLE ##GlobalTableName (
Column1 data_type,
Column2 data_type,
...
);
Here's an example of Local temp table :
[i] Let's assume you want to create a table that stores data temporarily and gets deleted automatically when you close the current query tab or logs out from the SQL Server database engine. It should be accessible within current query tab or session only.
[ii] Run below SQL statement :
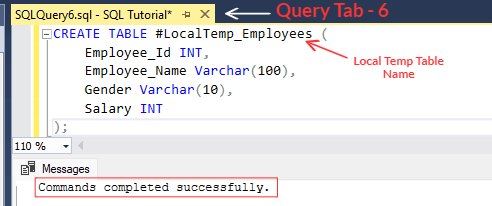
CREATE TABLE #LocalTemp_Employees (
Employee_Id INT,
Employee_Name Varchar(100),
Gender Varchar(10),
Salary INT
);
[iii] Above statement will create a new temp table named as '#LocalTemp_Employees'.
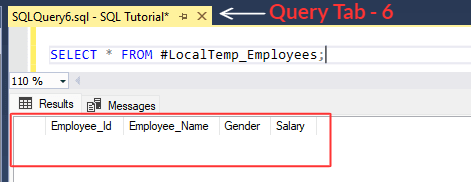
[iv] Next, let's run the below statement in the current query tab that selects '#LocalTemp_Employees' table.
SELECT *
FROM #LocalTemp_Employees;
[v] Above statement selects '#LocalTemp_Employees' table.
We know that 'Local temporary tables' are accessible exclusively within the current query tab or session.
[vi] Let's demonstrate this, run the below statement in a different or newer query tab.
SELECT *
FROM #LocalTemp_Employees;
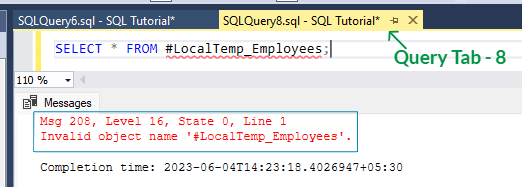
[vii] Above statement thrown an error stating 'Invalid object name' . This occurred because the '#LocalTemp_Employees' table is not present in this session ( 'Query Tab - 8' ).
Remember :
This '#LocalTemp_Employees' temporary table will be automatically deleted when the user closes the current query tab or session.
Here's an example of Global temp table :
[i] Let's assume you want to create a table that stores data temporarily and gets deleted automatically when you close the current query tab or logs out from the SQL Server database engine. It should be accessible to all the query tabs or session.
[ii] Run below SQL statement :
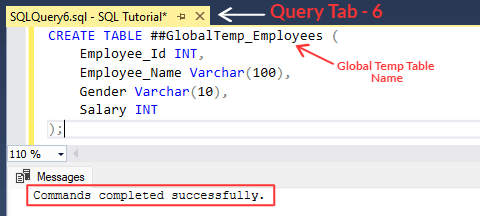
CREATE TABLE ##GlobalTemp_Employees (
Employee_Id INT,
Employee_Name Varchar(100),
Gender Varchar(10),
Salary INT
);
[iii] Above statement will create a new temp table named as '##GlobalTemp_Employees'.
[iv] Next, let's run the below statement in the current query tab that selects '##GlobalTemp_Employees' table.
SELECT *
FROM ##GlobalTemp_Employees;
[v] Above statement selects '##GlobalTemp_Employees' table.
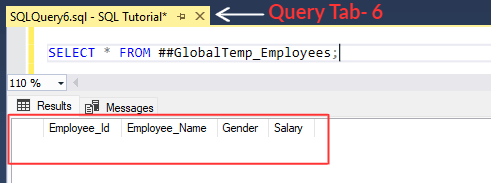
We know that 'Global temporary tables' are accessible to all the query tabs or session.
[vi] Let's demonstrate this, run the below statement in a different or newer query tab.
SELECT *
FROM ##GlobalTemp_Employees;
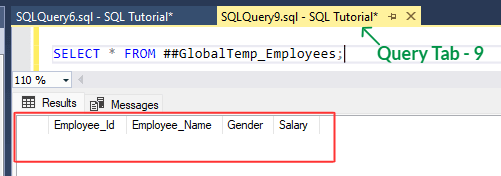
[vii] Above statement selects '##Global_Employees' table, even if this table is not present in this session ( 'Query Tab - 9' ).
Remember :
This '##GlobalTemp_Employees' temporary table will be automatically deleted when the user closes the current query tab or session.