Text copied!
SQL Subquery
In SQL, When a query is enclosed inside another query is called as 'Subquery' or 'Inner query'. The query that includes another query inside it, is referred to as 'Main query' or 'Outer query'.
'Outer query' uses the result of the 'Subquery' to perform data filtering or operations.
Here's the general syntax :
SQL query
( SQL query );
• Inner query is always enclosed in 'parenthesis ( )' to indicate it's boundaries and separation from outer query.
In SQL, 'Subqueries' can be used in SELECT, FROM, WHERE etc. clauses that enables user to merge and manipulate data with considerable power.
Here's an example of Subquery in SELECT clause :
Using subquery in 'SELECT' clause is known as 'scalar subquery'. It retrieves a single value from a subquery and include it as a column in the result-set of the outer query.
Here's the syntax :
SELECT column1, ( SELECT column2 FROM table2 WHERE condition ) AS subquery
FROM table1;
Suppose we have two tables : [i] Employees table [ii] Employees_2 table
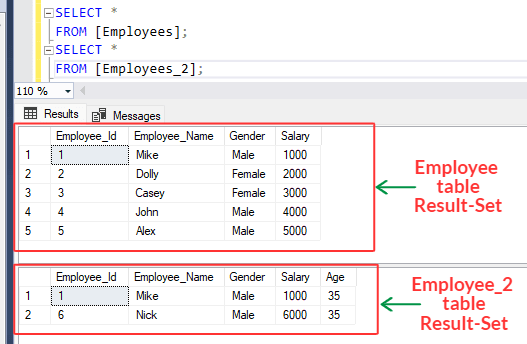
Run below SQL statement :
SELECT Emp.Employee_Name AS [Name], ( SELECT SUM(Salary) FROM [Employees_2] ) AS Subquery
FROM [Employees] Emp;
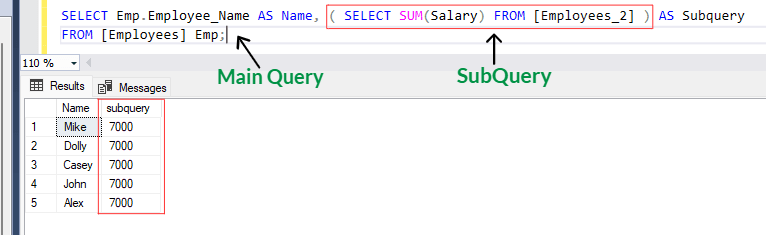
The subquery "( SELECT SUM(Salary) FROM [Employees_2] )" retrieves the sum of Salary from [Employees_2] table. The result of the subquery is then included as a column named "subquery" in the result-set of the outer query.
Here's an example of Subquery in FROM clause :
Using subquery in 'FROM' clause is known as 'derived table' or 'inline view'. It is used to create a temp table and then utilize in the outer query.
Here's the syntax :
SELECT column3
FROM ( SELECT column1, column2, column3 FROM table1 WHERE condition ) AS table_alias;
Run below SQL statement :
SELECT Salary
FROM ( SELECT Employee_Id, Employee_Name, Salary FROM [Employees] WHERE Gender = 'Male' ) AS xyz;
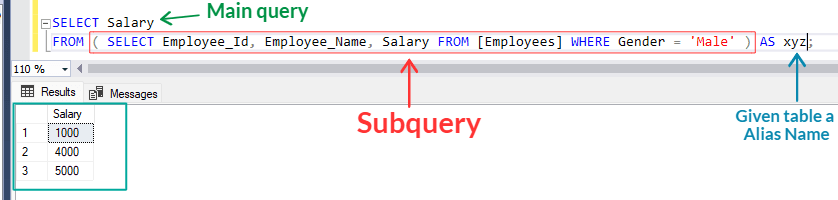
The subquery "( SELECT Employee_Id, Employee_Name, Salary FROM [Employees] WHERE Gender = 'Male' )" retrieves specific columns from [Employees] table. This subquery result is treated as temp table and outer query retrieves only Salary column from this temp table.
Here's an example of Subquery in WHERE clause, It is also known as 'Nested query' :
Using subquery in 'WHERE' clause is useful to filter the result-set based on the result of the another query. Using a query inside another query is known as a subquery or a nested query.
Here's the syntax :
SELECT column1, column2, column3
FROM table1
WHERE column1 IN ( SELECT column1 FROM table2 WHERE condition );
Run below SQL statement :
SELECT Employee_Id, Employee_Name, Salary
FROM [Employees]
WHERE Employee_Id IN ( SELECT Employee_Id FROM [Employees_2] WHERE Gender = 'Male' );
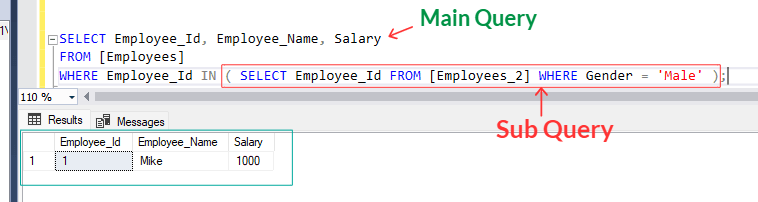
The subquery "( SELECT Employee_Id FROM [Employees_2] WHERE Gender = 'Male' )" retrieves all the Employee_Id values from [Employees_2] table. The outer query retrieves all specified column data from [Employees] table where Employee_Id matches with the Employee_Id of subquery result.