Text copied!
CASE statement
In SQL, CASE statement is used to perform different actions or return different values based on the specified conditions. It is very similar to the 'if-else' conditional structure.
The CASE statement examines each condition a sequential manner and performs the related action or returns the specified value when a condition is met.
The syntax of the CASE statement generally looks like this :
CASE
WHEN condition1 THEN result_expression1
WHEN condition2 THEN result_expression2
WHEN condition3 THEN result_expression3
...
ELSE result_expressionN
END
• 'CASE' keyword indicates that the case statement body has started.
• 'END' keyword indicates that the case statement body has ended.
• After the 'WHEN' keyword, specify the condition that you want to evaluate.
• After the 'THEN' keyword, specify the desired result to be executed when the condition evaluates to true.
• After the 'ELSE' keyword, specify result that denotes the result to be executed if none of the previous conditions evaluate to true. 'ELSE' keyword is an optional, If it is not specified and none of the previous conditions evaluate to true then the result is considered as NULL.
Here's an example of how you might use the CASE statement :
1. Let's assume we have a table named "[Employees]".
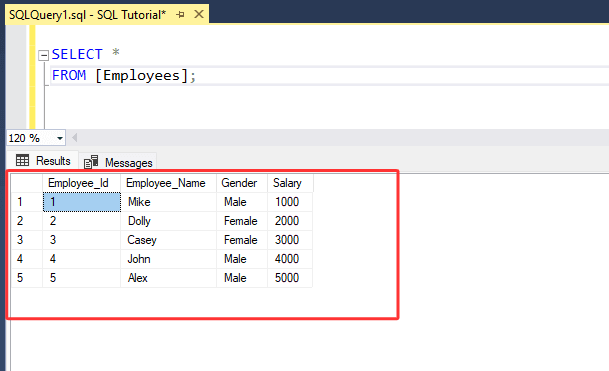
2. Let's assume you want to categorize employees based on their salary. "High" for salaries greater than 3000(inclusive) and "Low" for salaries less than 3000.
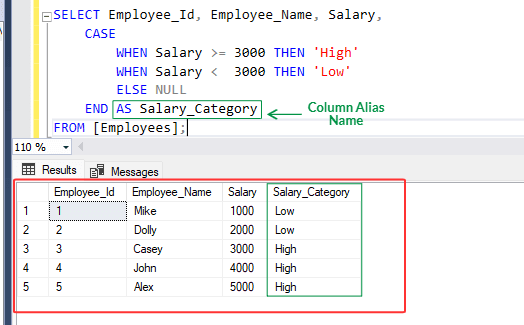
3. Run below SQL statement :
SELECT Employee_Id, Employee_Name, Salary,
CASE
WHEN Salary >= 3000 THEN 'High'
WHEN Salary < 3000 THEN 'Low'
ELSE NULL
END AS Salary_Category
FROM [Employees];
4. Above statement evaluates employee salaries from [Employees] table and assigns salary categories based on the specified conditions. Assigned an alias name of "Salary_Category" to this result.
The CASE statement is a powerful tool in SQL for decision making, simplifying the inclusion of conditional logic into queries and data manipulation operations.