Text copied!
ROW_NUMBER function
In SQL, the ROW_NUMBER function is used to assign a unique sequential integer to each row in the result set according to the specified criteria in ORDER BY clause.
The syntax of the ROW_NUMBER function generally looks like this :
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY column_name) AS row_number,
column1,
column2,
column3,
...
column N
FROM
table_name;
• ROW_NUMBER() is the window function that assigns a unique number to each row.
• ORDER BY column_name specifies the column(s) by which the rows should be ordered. This defines the sequence in which the row numbers will be assigned.
• AS row_number is an alias for the generated row number column.
Replace column_name with the actual column(s) by which you want to order your rows, and table_name with the name of your table.
Keep in mind that the ROW_NUMBER() function assigns unique numbers based on the order specified in the ORDER BY clause. If you want different numbering, you'll need to adjust the ORDER BY accordingly.
Here's an example of how you might use the ROW_NUMBER function :
1. Let's assume we have a table named "[Employees]".
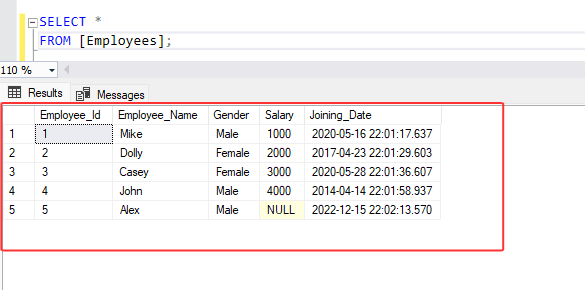
2. Let's assume you want to assign a unique sequential integer to each row in your query result set based on the order of the Salary column in the Employees table.
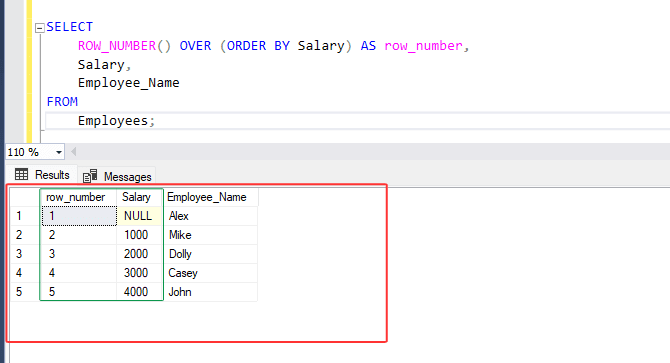
3. Run below SQL statement :
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY Salary) AS row_number,
Salary,
Employee_Name
FROM
Employees;
4. In the above statement, It creates a list of all employees and their salaries, giving each one a unique number. Employees earning less will be at the start of the list, and their numbers will begin from 1, going up as the salaries increase.
ROW_NUMBER function can be particularly useful for tasks like pagination or when you want to identify employees' rank based on their salary, assuming each salary value is unique or you're interested in the arbitrary order of employees with the same salary.
Remember :
Using this function in a select statement won't modify the [Employees] table directly, but it will only be reflected in the select statement's output.