Text copied!
HAVING clause
SQL clause is the specific part of a SQL statement which is used to perform various operations. It can be combined to create more complex queries to retrieve and manipulate data.
HAVING clause :
HAVING clause is always used with "GROUP BY" clause to filter the data that has already been grouped by the "GROUP BY" clause.
It is similar to the "WHERE" clause and used to filter the results of aggregate functions. While "WHERE" clause cannot be used with aggregate functions.
It is often used with other clauses such as 'SELECT', 'FROM' and 'ORDER BY' etc. to retrieve, specify table, sort and manipulate data.
The syntax of the HAVING clause generally looks like this :
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column_name(s)
HAVING conditions;
• Specify the column(s) name after the 'SELECT' keyword.
• Specify Asterisk (*) symbol to selects all columns from the table after the 'SELECT' keyword.
• Specify the table name after the 'FROM' keyword.
• Specify the column name(s) that you want to group and summarize after the 'GROUP BY' keyword.
• Specify the conditions after the 'HAVING' keyword.
Here's an example of how you might use the HAVING clause :
1. Let's assume we have a table named "[Employees]".
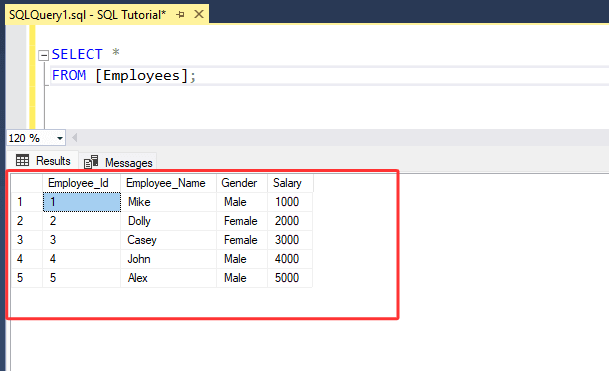
2. Let's assume you want to determine the number of employees by gender to know how many employees are male or female in the [Employees] table and then filter the data to identify where the count of males or females employees is equal to 2.
3. Run below SQL statement :
SELECT Gender, COUNT(Gender) AS [Gender_Count]
FROM [Employees]
GROUP BY Gender
HAVING COUNT(Gender) = 2;
4. In above statement, we used 'COUNT' function that returns the number of rows. Here, we specified the 'Gender' column in COUNT function.
5. 'Gender column' is specified in both of the SELECT and GROUP BY clauses that group and summarize the data by gender and 'COUNT' function returns the count of 'Male' and 'Female' employees separately. We filter the data by specifying a condition in the HAVING clause, only keeping records where the count is exactly 2.
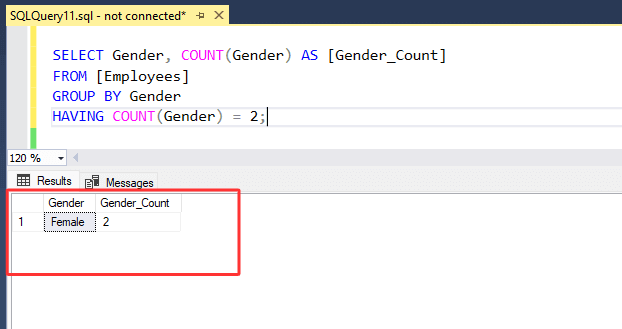
That's it! You have successfully retrieved the number of employees by gender and then filtered it from [Employees] table.