Text copied!
SQL Functions
In SQL, Function can be defined as a block/set of SQL statements that is used to perform a specific task or accomplish a particular purpose.
It can be reused through multiple projects which reduces code redundancy. 'Code redundancy' refers to the practice of writing the same code multiple times within a project.
Types of SQL functions :
1. User-defined function
2. System-defined function

1. User-defined function :
A user-defined function is a custom function created by a user. SQL Server allows you to create your own functions using the 'CREATE FUNCTION' statement that enables you to perform specific calculations.
2. System-defined function :
SQL Server provides extensive collection of built-in system functions is available that perform various tasks related to the database system. It is also famous as 'built-in functions'.
Here's the syntax :
CREATE FUNCTION function_name
(
@parameter1 data_type,
@parameter2 data_type,
...
)
RETURNS output_data_type
AS
BEGIN
-- Write SQL statements here to perform desired operation
RETURN output_value;
END;
• Specify the function name after the 'CREATE FUNCTION' keyword.
• Specify the parameter name using the "@" prefix and its data type within the parentheses ( ).
• Specify the return data type after the 'RETURNS' keyword. It is the output data type.
• 'AS BEGIN' keyword indicates that the function body has started.
• 'END' keyword indicates that the function body has ended.
• Specify the value after the 'RETURN' keyword. It is the output value that function will return.
Input Parameter :
In SQL Server, function accepts many or no parameter to execute specific calculation and returns a single result. A parameter is a value that is passed into a function, on which a specific task is performed.
Return type :
In SQL Server, every function must return a value. This means that if the output of the function is a number, you should define the return type as INT.
Calling function :
Calling function simply means executing or running it. To call a function in SQL Server, you can use the 'SELECT' statement in a SQL query.
Here's the syntax :
SELECT schema_name.function_name( arguments );
• Specify the schema name and function name after the 'SELECT' keyword.
• Specify the argument in 'parenthesis ( )'. An argument is a value that is passed into a function.
Here's an example of SQL user-defined function :
[i] Let's assume you want to create a function that adds two numbers.
[ii] Run below SQL statement :
CREATE FUNCTION AddtwoNumbers
(
@num1 INT,
@num2 INT
)
RETURNS INT
AS
BEGIN
RETURN @num1 + @num2;
END;
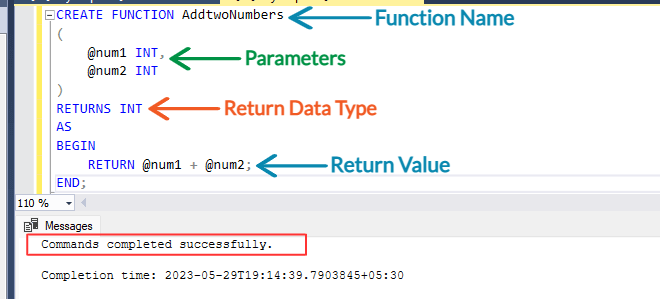
[iii] Above statement will create a new function named as 'AddtwoNumbers'.
[iv] Next, let's execute this function. Run below SQL statement :
SELECT dbo.AddtwoNumbers(1, 4);
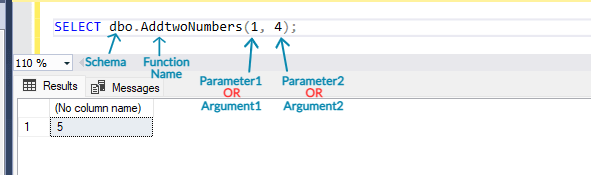
[v] Above statement adds values '1' and '4', hence value '5' is returned as output. Example : 1 + 4 = 5