Text copied!
RANK function
In SQL, the RANK function is used to assign rank to each row in a result set according to the specified criteria in ORDER BY clause.
It assigns a unique rank to each distinct row in the result set according to the ordering specified in the ORDER BY clause. If two rows have the same values for the ordering criteria, they will be assigned the same rank, and the next rank will be skipped.
The syntax of the RANK function generally looks like this :
SELECT
column1,
column2,
column3,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY partition_column ORDER BY order_column [ASC | DESC]) AS rank_column
FROM
table_name;
• PARTITION BY: This clause divides the result set into partitions to which the RANK() function is applied separately. The function will restart numbering the ranks for each partition.
• ORDER BY: This clause specifies the order in which the rows are ranked within each partition.
• rank_column: This is an alias for the resulting rank column.
Here's an example of how you might use the RANK function :
1. Let's assume we have a table named "[Student]".
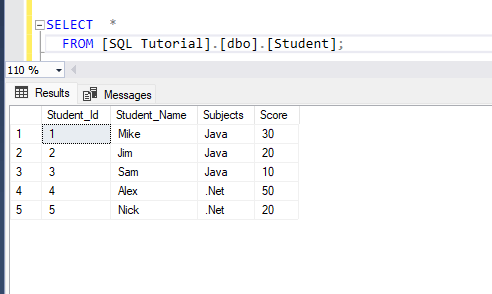
2. Let's assume you want to assign a rank to the students based on their scores within each subject.
3. Run below SQL statement :
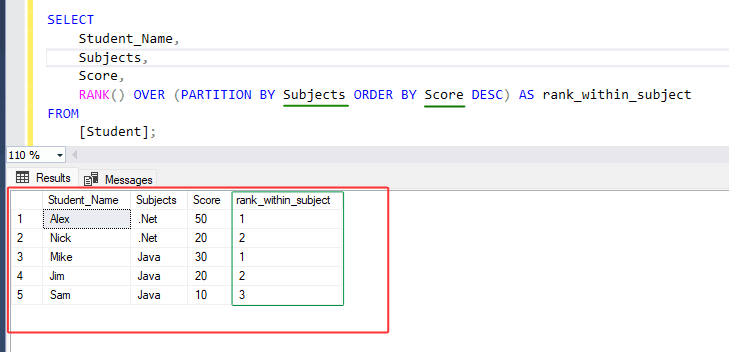
SELECT
Student_Name,
Subjects,
Score,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY Subjects ORDER BY Score DESC) AS rank_within_subject
FROM
[Student];
4. In the above statement, It assigns a rank to each student within each subject based on their score, with the highest scorer receiving rank 1, the next highest scorer receiving rank 2, and so on.
The RANK() function in SQL assigns ranks to data based on specified criteria, aiding tasks like identifying top performers, implementing pagination, analyzing market share, and comparing competitors, crucial for informed decision-making.
Remember :
Using this function in a select statement won't modify the [Student] table directly, but it will only be reflected in the select statement's output.